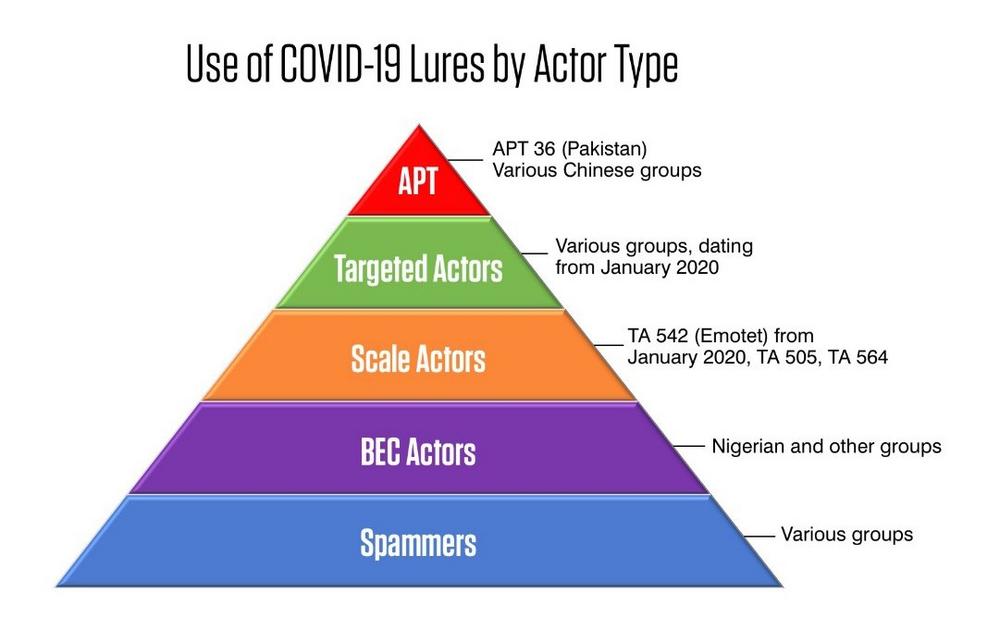
Threat Volumes
Coronavirus-themed attacks are dominating the threat landscape in a way that is nearly unprecedented. More than 80 percent of the threat landscape is using coronavirus themes in some way. This includes attacks that don’t outright mention coronavirus in the subject or body of a message, but instead reference it within attachments, links or lures.
To date, we have seen over 500,000 messages, 300,000 malicious URLs, 200,000 malicious attachments with coronavirus themes across more than 140 campaigns (and the number continues to increase). These attacks and campaigns are global in scope.
We have seen nearly every type of attack being used with coronavirus themes, including (but not limited to) business email compromise (BEC), credential phishing, malware, and spam email campaigns. Overall, we’ve seen a significant amount of credential phishing in these attacks. The threat actors behind these attacks run the gamut from small unknown actors to prominent threat actors like TA542 (the group behind Emotet) to APT actors like APT36.
Below is a breakdown of attack types and threat actors. These are ordered in a way that represents the scale and scope of what we’re seeing in the landscape.
Recent Notable Campaign Samples Leveraging Coronavirus
Credential Phish: Microsoft Office “COVID-19 Infected Our Staff”
Key Points: This small campaign in the United States primarily targets retail companies and uses concerns about infected staff members to try and lure victims to click. It leads to Microsoft Office credential phishing.
Summary: This credential phishing campaign uses the subject line “COVID-19 Infected Our Staff” and indicates a “staff member of our company has contracted this deadly disease (COVID-19)” and then encourages the recipient to open/download a malicious attachment to “follow the company’s new protocol.” The malicious attachment links to a webpage that spoofs the Microsoft Office login and asks the user for their credentials.
Malware: Remcos “Your Neighbors Tested Positive”
Key Points: This small campaign targeting energy, construction, and telecoms in the United States uses the subject line "coronavirus update disease (COVID-19) your neighbors tested positive" and has a malicious attachment "receipt.xlsm" that uses macros to download the Remcos remote control tool.
Summary: This campaign uses concerns around the possible infection of neighbors as its social engineering hook. The email’s subject line reads, “your neighbors tested positive” and encourages the recipient to open the malicious Microsoft Excel attachment. If the recipient opens the attachment and enables macros, the spreadsheet will download and install Remcos a remote control tool abused by threat actors to gain control over the system.
Malware: GuLoader/Agent Tesla with WHO “Solution” for COVID-19
Key Points: This medium-sized campaign in the United States primarily targets the manufacturing industry but also construction, transportation, healthcare, automotive, energy, and aerospace companies with GuLoader and Agent Tesla. The email spoofs the real address of the head of the World Health Organization (WHO), claims there is a “solution” for “total control” and asks the recipient to “share with all contacts.”
Summary: This campaign is similar to ones we saw in mid-February 2020 that spread conspiracy theories around possible cures for COVID-19 and abused the World Health Organization (WHO) brand.In this case, the sender spoofs the real email address of the head of the World Health Organization to make the message appear authentic. The email claims that the WHO has a “solution” for COVID-19 and encourages the recipient to open the malicious attachment for that information and share with “all contacts to ensure rapid control of the epidemic.” The malicious attachment contains GuLoader compressed in .iso format. If the recipient opens and runs the attachment, GuLoader installs Agent Tesla, a Trojan written in Visual Basic that can steal usernames, passwords, and credit card information from the user’s system.
Malware: GuLoader in Spain and Portugal
Key Points: This small campaign weighted towards manufacturing and industrial targets in Spain and Portugal and features GuLoader.
Summary: This Spanish-language campaign features emails with the subject "Vacuna COVID-19: prepare la vacuna en casa para usted y su familia para evitar COVID-19" (English translation: "COVID-19 vaccine: prepare the vaccine at home for you and your family to avoid COVID-19"). The message body discusses preparation of a homemade COVID-19 vaccine. The recipient is urged to open the malicious attachment titled COVID- 19.exe inside COVID- 19.tar, which is a .tar file that contains a compressed version of GuLoader. GuLoader is a recently developed and now-popular downloader written in Visual Basic (VB) 6.0.
Credential Phish: Anti-bacterial Debit Card (Netherlands)
Key Points: This small campaign in Dutch has targeted manufacturing, technology, and industrial companies in the Netherlands and is designed to steal banking credentials.
Summary: This credential phishing campaign targets manufacturing, technology, and industrial companies in the Netherlands for banking credentials. The attack uses email lures in Dutch posing as a major bank in the Netherlands, with a subject of "Bericht over coronavirus." (English translation: Coronavirus message). The message body introduces a new "antibacterial debit card, which you have until 19 March 2020 to apply for this debit card free of charge." The message contains a link, which the recipient is urged to click for this debit card. When clicked, users are taken to a spoofed page of the bank in question and asked to enter their banking credentials.
Conclusion
Coronavirus threats continue to predominate the threat landscape and show no sign of slowing down. As updates around the pandemic continue to change day-to-day across regions, threat actors’ themes and attacks have changed to match as well. For example, in the first few days of activity related to the virus, we saw threat actors focusing on concerns around the impact of COVID-19 on shipping and manufacturing. Now we see threat actors focusing on the concerns around supposed cures and infected individuals. As more and more employees are being asked to work from home and governments around the world work to provide support for its citizens, we can expect that threat actors will adapt and use these as themes in the not too distant future.
Proofpoint
Zeppelinstr. 73
80333 München
Telefon: +49 (871) 78064258
http://www.proofpoint.com/de
![]()